This part-time course meets the requirements of the Level 7 System Engineering Master's Apprenticeship Programme. Eligible organisations will be able to use their Apprenticeship Levy to cover the cost of the course tuition fees. Find out more about Master's Apprenticeships.
Overview
- Start dateSeptember
- DurationMSc: up to three years part-time
- DeliveryBlended learning
- QualificationMSc
- Study typePart-time
- CampusCranfield campus
Who is it for?
- Experienced and/or qualified engineers, scientists, managers or leaders wishing to broaden and deepen their skills or apply them in systems engineering or related roles.
- Recent graduates wishing to extend their knowledge and skill within systems engineering professional roles.
Why this course?
The Centre for Systems Engineering has been at the forefront of developing systems engineering education for the past fifteen years, blending the breadth of systems thinking with the rigour of systems engineering and closely integrating this within acquisition management.
The course has been set up to enable students better understanding to focus content and delivery on systems engineering professionals working in distributed, agile teams using shared models and flexible working approaches, with an emphasis on professional skills such as leadership, team working, communication, data management and ethics.
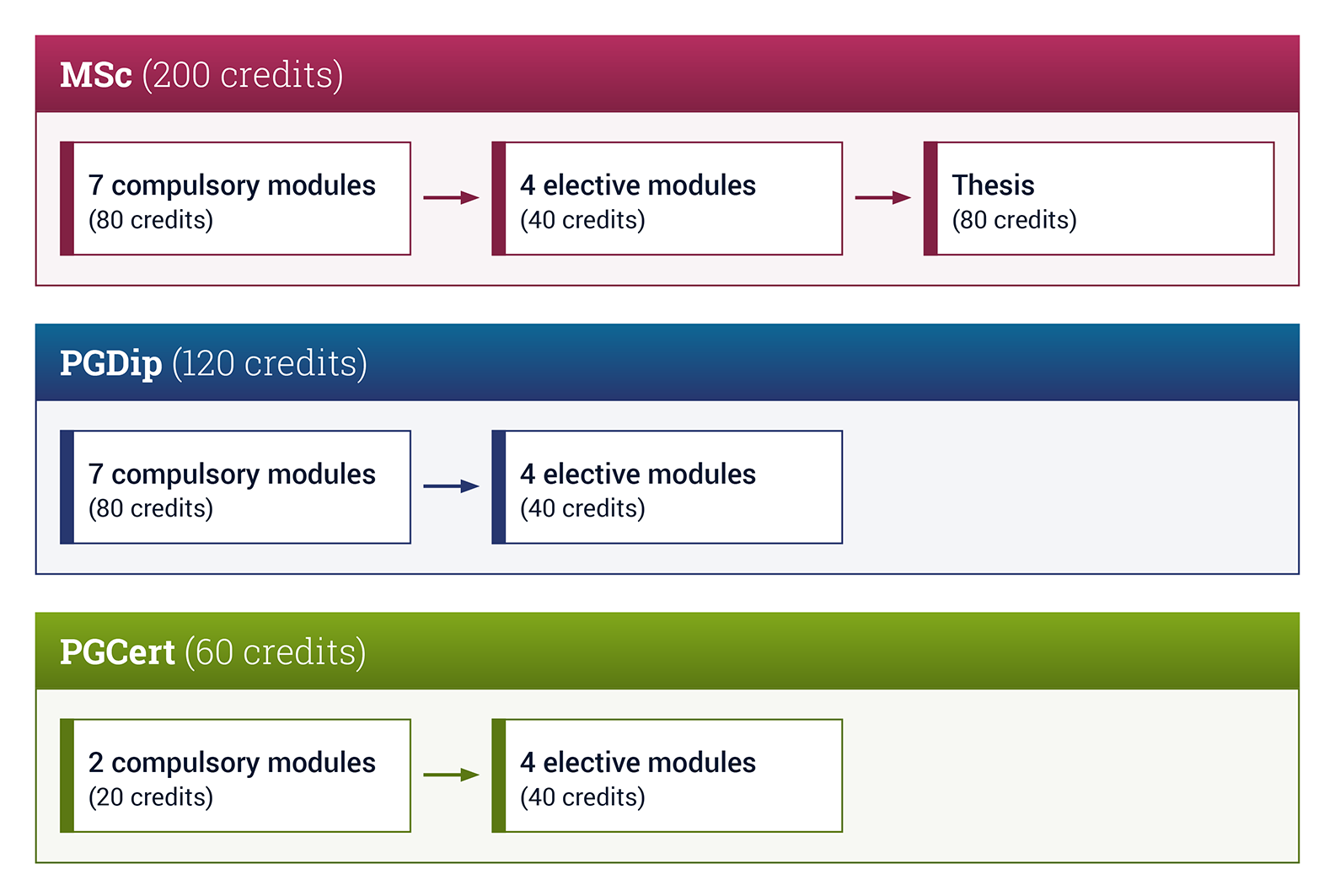
The MSc in Systems Engineering is designed for those seeking Professional status in their chosen career. A PgDip (two years) is usually the minimum qualification used for mapping to the UKSPEC.
However, the University recognises that personal circumstances may change and as such there is a possible exit route after one year’s successful completion of study, of a PgCert in Systems Engineering.
Institute for Apprenticeships - Systems Engineering Degree
Course details
Our apprenticeship is delivered by blended learning, primarily using both distance learning and face-to-face tutorials based at our Cranfield campus in Bedfordshire. The duration of the apprenticeship is three years not including End Point Assessment.
Apprentices will take their learning from the course into their organisation and apply their learning through workplace practice, evidencing their new-found knowledge, skills and behaviours as part of their portfolio of evidence.
Course delivery
Blended learning
Individual project
The Individual Project provides you with an opportunity to undertake an in-depth study of an area of particular interest to you or your sponsor which is written up as a thesis or dissertation. The study might include, for example:
- Application of systems engineering tools and techniques to a real-world problem,
- Analysis of underpinning systems engineering theory and practice,
- Development of new or tailored systems engineering processes.
Modules
Keeping our courses up-to-date and current requires constant innovation and change. The modules we offer reflect the needs of business and industry and the research interests of our staff and, as a result, may change or be withdrawn due to research developments, legislation changes or for a variety of other reasons. Changes may also be designed to improve the student learning experience or to respond to feedback from students, external examiners, accreditation bodies and industrial advisory panels.
To give you a taster, we have listed the compulsory and elective (where applicable) modules which are currently affiliated with this course. All modules are indicative only, and may be subject to change for your year of entry.
Course modules
Compulsory modules
All the modules in the following list need to be taken as part of this course.
Introduction to Systems and Systems Engineering
| Module Leader |
|
|---|---|
| Aim |
|
| Syllabus |
Unit 1: Systems Science
Unit 2: Systems Thinking
Unit 3: SE Life Cycle
United 4: Systems Modelling
|
| Intended learning outcomes |
On successful completion of this module you will be able to:
|
System Definition
| Module Leader |
|
|---|---|
| Aim |
|
| Syllabus |
Overview of early Life Cycle management and how SE Concept and System Definition are related in a Model Based approach, Overview of Logical Architecture and Requirements theory and models. Unit 2: Model Based SE (MBSE), Introduction to the System Modelling Language (SySML), Overview of the course MBSE methodology. Unit 3: Model Based System Definition - Requirements System Requirements Process outcomes and activities, Using MBSE models to define System of Interest Functions and Requirements, Unit 4 Requirements Management, Principle of Good Requirements Specification and Review. Unit 5: Model Based System Definition - Architecture: Logical System Architecture Process outcomes and activities, Using architecting notations to define Logical Architectures (LA), iterations between LA, Physical Architecture and Mission Analysis. Unit 6: Module Workshops, Apply Requirements and LA models in a group student project, Discussion of MBSE Benefits and Challenges. Note, for the SEE module these units are covered in weeks 1-6. For the SESD they are delivered over a 5 day residential timetable, with workshops each day. |
| Intended learning outcomes |
On successful completion of this module you will be able to:
|
Systems Thinking in Practice
| Module Leader |
|
|---|---|
| Aim |
|
| Syllabus |
Unit 1: Problem Exploration
Unit 2: Concept Definition: Mission Analysis (MA)
Unit 3: Reflection |
| Intended learning outcomes |
On successful completion of this module you will be able to:
|
Enterprise Systems Engineering
| Module Leader |
|
|---|---|
| Aim |
Successful integration and practice of systems engineering within a business environment requires a wider knowledge and understanding of the strategic management and business processes of the organisation and wider enterprise. Spanning a wide range of individual disciplines, enterprise management is used to ensure that all business activity is planned, managed and delivered to achieve strategic aims, objectives and goals. The interdisciplinary nature and wide-ranging applicability of systems engineering means there are inevitable touch points and integration requirements to ensure the enterprise can continue to deliver and meet its overarching goals and requirements. This module critically examines the relevance of underpinning theories and practice across the enterprise management domain from a systems engineering perspective. Taking a capability- and effects-based context, it aims to provide the systems engineer with extended knowledge of the wider business environment within which the systems lifecycle sits, and how systems engineering application itself requires systems thinking and practice to successfully integrate it within wider business and management processes and approaches |
| Syllabus |
Unit 1 – Enterprises, Architectures and Lifecycles Unit 2: Strategy and Mission Analysis Unit 3 – Operations Management and Systems Engineering Unit 4 – Capability Management and Stakeholder Needs Note, for the SEE module these units are covered in weeks 1-6. For the SESD they are delivered over a 5 day residential timetable, with workshops each day. |
| Intended learning outcomes |
On successful completion of this module you will be able to:
|
System Design and Realisation
| Module Leader |
|
|---|---|
| Aim |
|
| Syllabus |
Unit 1: System design,
Unit 2: Trade Studies,
Unit 3: Integration, Verification and Validation,
Unit 4: Through life support,
Unit 5: Logistics, obsolescence and system retirement,
Unit 6: Other considerations: Acceptance, training, impact of organisational role allocations, |
| Intended learning outcomes |
On successful completion of this module you will be able to:
|
Systems Engineering Application Workshop
| Aim |
|
|---|---|
| Syllabus |
|
| Intended learning outcomes |
On successful completion of this module you will be able to:
|
Systems Research Methods
| Aim |
This module provides a multi-perspective, multi-methodological approach to research as the basis for the range of research questions that may be addressed in the student's thesis and also in investigations in future professional work. This module supports both these needs through challenging the student to think about research tasks and methods suitable for achieving the goal of obtaining actionable knowledge about a variety of research topics. |
|---|---|
| Syllabus |
Unit 1: Knowledge, novelty and verification and validation Unit 2: Areas of interest and research questions Unit 3: Framing research projects Unit 4: Quantitative methods Unit 5: Modelling and simulation method Unit 6: Formative feedback re proposed research methodology Unit 7: Writing about research: Proposals, reports, theses, and papers |
| Intended learning outcomes |
On successful completion of this module a student should be able to:
|
Thesis
| Module Leader |
|
|---|---|
| Aim |
To conduct a self-directed piece of research applying the principles, practices and processes developed in the course to a real world problem of interest and relevance to the student. |
| Syllabus |
|
| Intended learning outcomes |
On successful completion of this module you will be able to:
|
Elective modules
One of the modules from the following list needs to be taken as part of this course.
Software and Cyber Systems Engineering
| Aim |
|
|---|---|
| Syllabus |
Unit 1: Software Engineering and Systems Engineering,
Unit 2: System Analysis and Modelling,
Unit 3: Software Architectures and Models,
Unit 4: Cyber Systems and Security,
Unit 5: Integration and Testing,
Unit 6: Other Considerations, |
| Intended learning outcomes |
On successful completion of this module you will be able to:
|
Megaproject Systems
| Module Leader |
|
|---|---|
| Aim |
Megaprojects are large, complex projects that typically have a value of above $1Bn. Once considered rarities, megaprojects are not only large, but growing constantly larger and are being constructed in ever greater numbers. From high-speed rail to modern major defence projects, or from staging the Olympics to implementing national 5G communications networks, megaprojects affect our normal everyday lives and can impact millions of people. What sets megaproject systems apart from more traditional system is not just their size but their complexity and scope – megaprojects often straddle public and private sector boundaries and are intrinsically linked to the general public. This means that technological, political, economic and societal aspects all coalesce and play an important role - both overtly and covertly – to system success. This module explores the realm of megaproject systems and expands the traditional systems engineering approaches, thinking and methods to identify and address the complexity and closer integration of hard engineering, design, management and social sciences within a single entity. |
| Syllabus |
Unit 1 – The Megaproject Engineering Mindset
Unit 2 – Planning and Delivery
Unit 3 – Towards the Boundary and Beyond: Context
Unit 4 – Accounting for Change |
| Intended learning outcomes |
On successful completion of this module you will be able to:
|
Life Cycle Cost and System Value
| Module Leader |
|
|---|---|
| Aim |
|
| Syllabus |
Value and utility – financial value and cost of systems and benefits provided in the application domain, Alternatives in design and engineering, Interest, compound interest, time value of money, Formulae for equivalent value over time. Unit 2: Methodology, Life cycle cost situation, Life cycle cost analysis, Cost over the life cycle, Estimating cost – methods analogy, parametric methods, accounting, data, reference class forecasting. Unit 3: Errors in estimation and sensitivity analysis, Errors in estimation – methods to describe, Sensitivity analysis – single and multiple alternatives, Monte Carlo analysis and applications. Unit 4: Additional Factors Affecting Decisions, Depreciation (real and book value), Taxation effects on analysis, Projects with no financial return (typically government asset and service provision), Inflation. Unit 5: Application to complex System Planning, Optimisation of investment decisions, Planning of fleet size, Economic life calculations. Unit 6: System Life Cycle Events, Effect of change of scenario during life, Valuation of system resilience. |
| Intended learning outcomes |
On successful completion of this module you will be able to:
|
Dependability and Resilience
| Module Leader |
|
|---|---|
| Aim |
|
| Syllabus |
The concepts of function, failure, fault and defect in the context of reliability, maintenance, maintainability, availability and resilience. Relationship of availability, reliability and maintainability and systems engineering, Contracting for availability, reliability and maintainability. Unit 2: Reliability and maintainability, Mechanisms of failure and their mathematical description, Concepts and introductory analysis of fault tree analysis, Corrective and preventive maintenance, Maintenance strategies to provide equipment repair, overhaul and Through Life Support, Level of Repair Analysis, Failure Modes Effects and Criticality Analysis. Unit 3: Availability, Measures of availability, Intrinsic Availability, Achieved Availability, Operational Availability, Discussion of the relationship between the different views of availability in the three measures. Unit 4: Introduction to Resilience, Overview of resilience, Concept of threat, Time phases of resilience: before, during, after threat events, Type A and Type B threats, Active and latent threats, Relationship of resilience and other specialty engineering fields. Unit 5: Resilience Schools of Thought (1) Hollnagel School of Thought based on safety and organisational response, Protection School of Thought focused on identifying high impact threats and providing methods to protect from their effect. Unit 6: Resilience Schools of Thought (2) Engineering for Resilience through use of design heuristics, Measurement of resilience – diverse approaches to measurement of resilience and the implied definition and view of resilience. |
| Intended learning outcomes |
On successful completion of this module you will be able to:
|
Human Systems Engineering
| Aim |
Provide students with an understanding of the challenges raised by the consideration of humans in systems, and the tools and techniques for considering human system issues across the SE life cycle as part of a Model Base SE approach. |
|---|---|
| Syllabus |
Review of system, human-machine system and systems engineering, Overview of human factors contribution in systems engineering, Introduction of some key terminologies, HF, HFE, ergonomics, HFI and HSI and the history of their development. Unit 2: Human Considerations in Engineering, Overview of human factors areas that need considerations in Engineering System The application of human factors in rail and highway industry, The application of human factors in defence industry. Unit 3: Human Cognitive Aspects and Organisational and Cultural Issues, Overview of human cognitive aspects in complex socio-technical systems, Overview of cultural and organisational behaviour aspects in complex socio-technical systems, Overview of human requirements. Unit 4: Human Factors Methods, Human factors methods and tool and their relationship with systems engineering, Human factors methods for supporting human systems engineering, Systems engineering methods for supporting human systems engineering. Unit 5: Human Factors in the SE Life Cycle, A general discussion of the mapping HF Methods to the SE life Cycle, Suggested generic HF activities and views, as part of the MBSE methodology presented earlier in the module, Example of the HF extension to the MBSE methodology. Unit 6: Human Factors Integration to SE Workshop, The application of SE methods, including MBSE, for supporting Human Systems Engineering, The application of HF methods integration into the SE life cycle for supporting Human Systems Engineering. |
| Intended learning outcomes |
On successful completion of this module you will be able to:
|
Dynamic Modelling of Systems
| Module Leader |
|
|---|---|
| Aim |
|
| Syllabus |
Dynamical systems, complexity and change. Closed systems and their behaviour. Structure as a driver of dynamic behaviour. Building candidate understanding models and testing them. Reference modes. The "twin pillars" of SD – feedback thinking and computational modelling. SD as a paradigm to support systems thinking, Unit 2: Qualitative SD, Seeing complexity as an emergent consequence of cause and effect. Visualising the interdependencies within complex systems using feedback structures and causal loop diagrams. Considering policy interventions as points of leverage. Developing understanding of complex systems and communicating it usefully. Relationship to other soft methods, Unit 3: Quantitative SD, Simulating feedback systems. First order, second order and higher order feedback systems. Suggesting and testing policy interventions for behavioural improvement. Theoretical underpinnings of SD modelling, including its background in control theory. Introducing delays. Formulating equations, using data and estimating parameters. Relationship to other computational simulation methods, Unit 4: Implementing the SD approach, Building useful models. Verification and validation of simulation models. Case studies and a detailed modelling exercise. |
| Intended learning outcomes |
On successful completion of this module you will be able to:
|
Simulation in the Systems Engineering Lifecycle
| Module Leader |
|
|---|---|
| Aim |
|
| Syllabus |
Unit 1: Foundations of Simulation Modelling, Unit 2: Appreciation of Modelling in the SE Context, Unit 3: Introduction to Modelling Paradigms, Unit 4: Model building and analysis, |
| Intended learning outcomes |
On successful completion of this module you will be able to:
|
Complex Adaptive Systems
| Module Leader |
|
|---|---|
| Aim |
As products, services and solutions become ever more detailed and interconnected in their nature, ideas of complexity become ever more important in understanding the structure and behaviour of these artifacts. Moreover, as these artifacts are required to alter and adapt to changes in requirement, use and context, it is important that a means to allow them to be adapted as rapidly as possible is considered during their development and use lifecycle. Therefore, the idea of Complex Adaptive Systems (CAS) is necessary to meet the challenges in developing and supporting products, services and systems in an ever-changing world. This module will consider CAS in the context of current industrial and consumer need and appraise how SE methods and methodologies such as Agile can be used to describe, characterise, and implement them. This will be placed within the context of the systems lifecycle. |
| Syllabus |
Examine the nature of complexity in systems, Analyse the meaning of complex adaptive systems and consider the different forms that they might take, Appraise how systems engineering can facilitate the development and support of CAS. Unit 2: Complex Adaptive Systems Thinking, Evaluate how a complex adaptive system (CAS) can be characterised and described within representative business and enterprise contexts, Evaluate how SE methods and tools can help characterise CAS. Unit 3: Complex Adaptive Systems and Agile, Evaluate the worth, strengths and weaknesses of Agile methodologies such as SCRUM and SAFe in facilitating CAS, Apply agile methods to a representative case study, Reflect on the use of agile methods. Unit 4: Design for Complex Adaptive Systems (DfCAS), Analyse what is needed to institute a design philosophy that will support the development and implementation of CAS, Create a logical architecture to support DfCAS for a representative case study, Reflect on the extent to which architectures can be made reconfigurable. Unit 5: Through Life Planning, Evaluate the effect of Complex Adaptive Systems (CAS) on Through Life Systems Engineering and Management (TLSEM), Devise a representative systems lifecycle for CAS. |
| Intended learning outcomes |
On successful completion of this module you will be able to:
|
Teaching team
You will be taught by Cranfield's leading experts with capability expertise, industry knowledge and collective subject research, as well as external speakers from industry and defence. The Student Academic Support lead for the MSc in Systems Engineering is Karen Crouch and the Course Director is Steve Barker. The teaching team includes:
Your career
Takes you on to impressive career prospects across a range of roles commensurate with your experience. This includes membership of multidisciplinary teams in acquisition, supply or research organisations. This could be in both general systems engineering roles or as a focal point for specific skills such as availability, reliability and maintenance (ARM), human factors, requirements, architecture test and evaluation etc. It is also applicable to key roles in MoD acquisition such as project team leader, capability manager and requirements manager.
Cranfield Careers and Employability Service
Cranfield’s Career Service is dedicated to helping you meet your career aspirations. You will have access to career coaching and advice, CV development, interview practice, access to hundreds of available jobs via our Symplicity platform and opportunities to meet recruiting employers at our careers fairs. Our strong reputation and links with potential employers provide you with outstanding opportunities to secure interesting jobs and develop successful careers. Support continues after graduation and as a Cranfield alumnus, you have free life-long access to a range of career resources to help you continue your education and enhance your career.
How to apply
Next Steps
If you would like to find out more general information about the course and your eligibility to attend the programme, if you'd like specific information on the course please contact the course director
For employer related enquiries, fees and funding, and the expression of interest/application process, please contact our Apprenticeships Team
Employers: Please complete our Expression of Interest form.
Prospective students: Please ask your employer to submit an Expression of Interest form to indicate their willingness to sponsor you.
Applications for apprenticeship routes have to come via the Expression of Interest form. Apprenticeship applications received via the application button on the non-apprenticeship pages will not be processed.
Under the Apprenticeship Levy scheme employers can fund apprenticeships for any new and current staff with the right to work in the UK and whose main place of work is England. This programme meets the requirements of the Level 7 Systems Engineer (Degree) apprenticeship standard. Eligible organisations will be able to use their Apprenticeship Levy to cover the cost of the programme. If you think you could qualify for sponsorship under this scheme please consult the information pages on becoming an Apprentice.